PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
201-437-1
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Sulfonic acid is a compound with general formula RSO2OH, where R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a derivative of sulfuric acid (HOSO2OH) where an OH has been replaced by a carbon group or a compound where a hydrogen atom has been replaced by treatment with sulfuric acid; for example, benzene is converted to benzenesulfonic acid (water-soluble). Sulfonic acid has a sulfur atom bonded to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon and bonded also to three oxygen atoms, one of which has been attached to a hydrogen atom. Sulfonic acid is acidic due to the hydrogen atom, stronger than a carboxylic acid. Sulfonic acid is one of the most important organo sulfur compounds in organic synthesis. Sulfonic acids are used as catalysts in esterification, alkylation and condensation reactions. Sulfonates are salts or esters of sulfonic acid. Sulfonic salts are soluble in water. Sulfonic acid and its salts present in organic dyes provide useful function of water solubility and or improve the washfastness of dyes due to their capability of binding more tightly to the fabric.
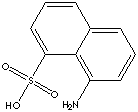
Peri Acid (1-naphthylamine-8-sulfonic Acid) is used directly in making several dyes and converted into numerous dye intermediates, as well as into tanning agents.
APPEARANCE
90% in (dry basis)
2811
Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-36
PRICE